**Unveiling the Salinity of the Oceans: Exploring How Much Salt Lies Within a Gallon**
As a child, I was fascinated by the ocean’s vastness. I would gaze out at the horizon and wonder what secrets lay beneath the surface. One question that always piqued my curiosity was: how much salt is dissolved in the ocean’s water? To my surprise, the answer is both fascinating and complex.
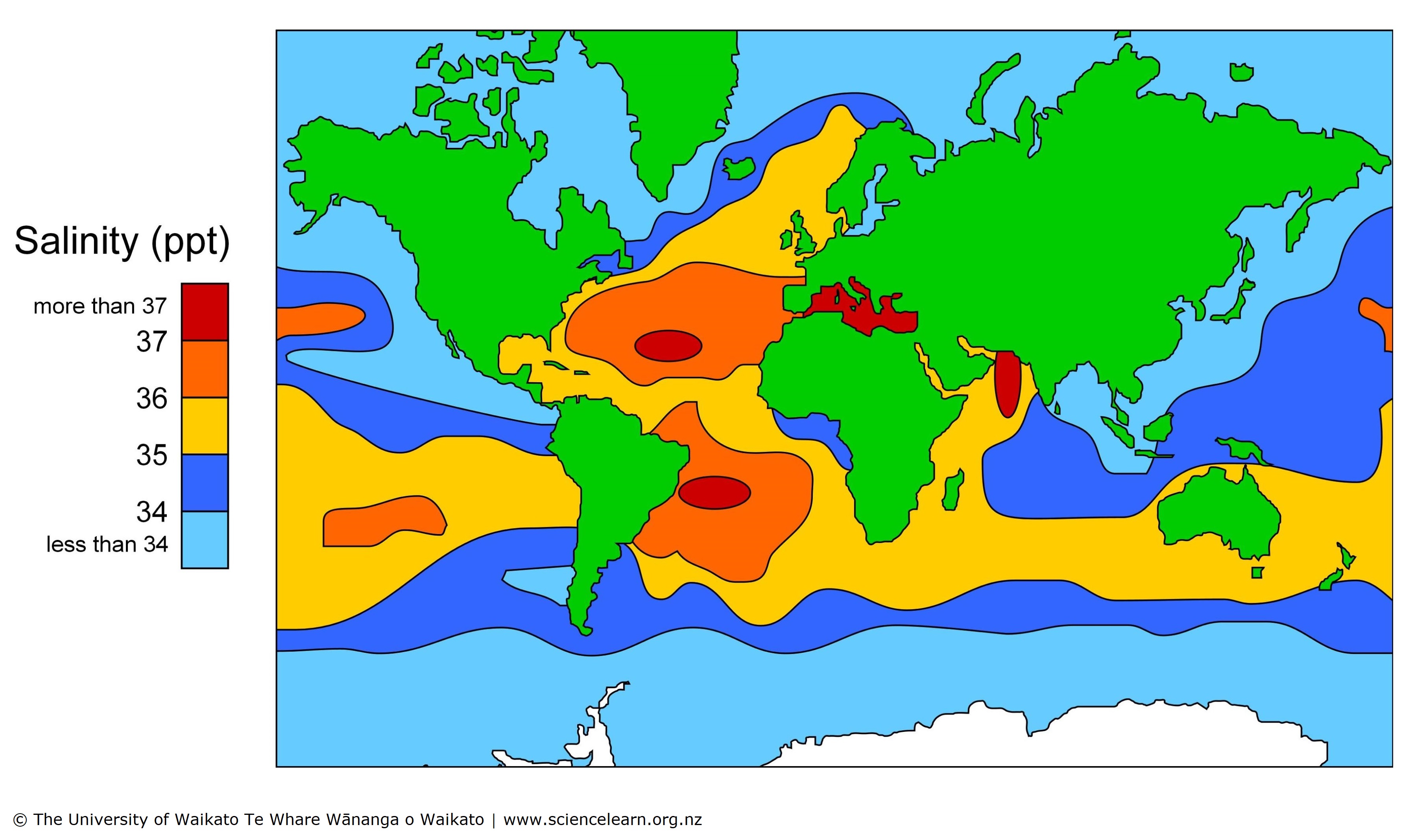
On average, a gallon of seawater contains approximately 35 grams of salt. This saltiness is primarily due to dissolved minerals, including sodium, chloride, potassium, and calcium. However, the salinity of seawater can vary depending on location and depth.
**Beneath the Waves: Salinity Variations**
The salinity of the ocean is not uniform throughout. Factors like evaporation, precipitation, and freshwater input from rivers and glaciers can influence the salt content of seawater. Near the equator, where evaporation rates are high, the water tends to be more saline than in polar regions, where precipitation and freshwater inputs are more significant.
Additionally, salinity can also vary with depth. In some areas, deeper waters can be more saline due to the accumulation of dissolved minerals over time. This is because the denser, more saline water sinks to the bottom, creating a vertical gradient in salinity.
**The Importance of Salt in the Ocean**
The saltiness of the ocean plays a crucial role in maintaining the Earth’s ecosystem. It affects the density, temperature, and pH of seawater, influencing the behavior and distribution of marine life. Furthermore, the salt in the ocean helps regulate the Earth’s climate by absorbing and releasing heat.
**Trends and Changes in Ocean Salinity**
Recent scientific research has highlighted changes in ocean salinity patterns. In some areas, sea surface salinity is increasing due to increased evaporation and reduced precipitation related to climate change. These changes can impact marine ecosystems, ocean circulation, and global weather patterns.
**Tips for Understanding Ocean Salinity**
To better understand ocean salinity, consider these expert tips:
- Measure salinity using a salinometer or refractometer.
- Consider the temperature and depth of the water when measuring salinity.
- Explore salinity data from online databases or scientific publications.
By following these tips, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the importance and dynamics of ocean salinity.
**Frequently Asked Questions**
- Q: Why is the ocean salty?
A: The salt in the ocean comes from dissolved minerals from rocks and soil, as well as from volcanic activity. - Q: How can I measure ocean salinity?
A: You can measure salinity using a salinometer or refractometer. - Q: Does ocean salinity affect marine life?
A: Yes, salinity is a vital factor that influences the distribution and behavior of marine organisms.
**Conclusion**
Understanding the amount of salt in the ocean is a fascinating and essential aspect of marine science. By exploring the factors that influence salinity and its importance, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of our planet’s vast and dynamic oceans. So next time you gaze out at the sea, remember the countless grams of salt dissolved within each gallon of water, serving as a hidden treasure that shapes the world beneath the waves.
Are you interested in learning more about the salinity of the ocean? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below.

Image: www.usgs.gov

Image: www.quenchsea.world
Salt Water Flush Recipe This means in every gallon of seawater, there are roughly 2.2 pounds (1 kilogram) of salt. This high salinity is what makes seawater undrinkable for humans and most land animals, but essential for the survival of various marine species like fish and algae. The salt content of seawater comes from the erosion of rocks on land, as well as volcanic