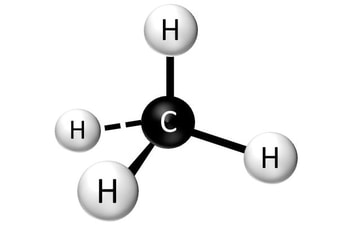
Jul 31, 2022Molecular Structures. Carbohydrates can be represented by the formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule.In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate“: the components are carbon (“carbo”) and the components of water (hence, “hydrate”).
What are the products of glycolysis? – Quora
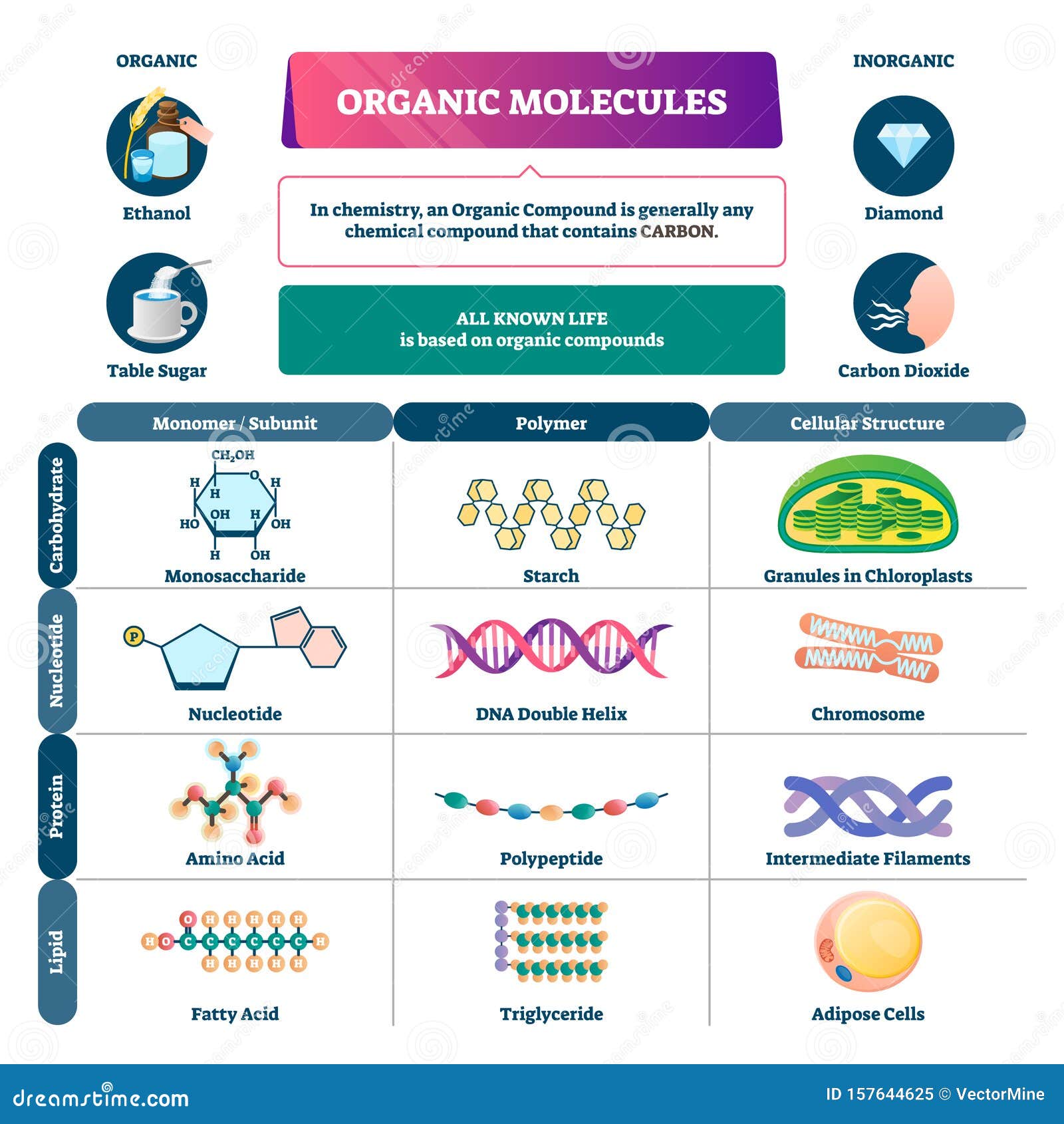
A monosaccharide, the monomer of carbohydrates, is a simple sugar such as fructose or glucose. Fructose is mostly found in fruits, whereas glucose generally results from the digestion of other carbohydrates. Glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6) is used for energy by the cells of most organisms and is a product of photosynthesis. Discuss further with Flexi
Source Image: dreamstime.com
Download Image
Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate“: the components are carbon (“carbo”) and the

Source Image: tiktok.com
Download Image
SOLUTION: Macromolecules google docs – Studypool Jan 2, 2024Carbohydrate | Definition, Classification, & Examples | Britannica Home Health & Medicine Anatomy & Physiology Science & Tech carbohydrate biochemistry Cite External Websites Written by Eugene A. Davidson
Source Image: mrgscience.com
Download Image
The Monomer Of A Carbohydrate Is A
Jan 2, 2024Carbohydrate | Definition, Classification, & Examples | Britannica Home Health & Medicine Anatomy & Physiology Science & Tech carbohydrate biochemistry Cite External Websites Written by Eugene A. Davidson Home Bookshelves General Chemistry Structure & Reactivity in Organic, Biological and Inorganic Chemistry (Schaller) Structure & Reactivity in Organic, Biological and Inorganic Chemistry I: Chemical Structure and Properties
GR 9 Topic 3: Macro Molecules – AMAZING WORLD OF SCIENCE WITH MR. GREEN
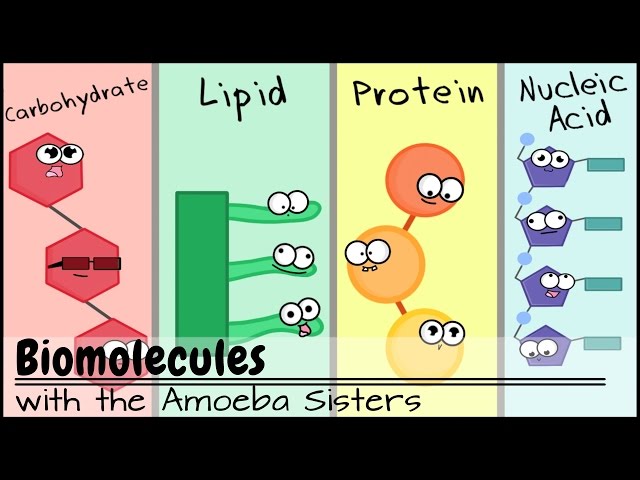
AboutTranscript. A carbohydrate is a type of molecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates can be simple sugars (monosaccharides) like glucose, or they can be made up of multiple sugar units (polysaccharides) like glycogen. They are important in biology as a source of energy and as structural components in plants. Materials | Free Full-Text | Hemp Fibre Properties and Processing Target Textile: A Review

Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
What Are Monomers Of Carbohydrates? – Database Football AboutTranscript. A carbohydrate is a type of molecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates can be simple sugars (monosaccharides) like glucose, or they can be made up of multiple sugar units (polysaccharides) like glycogen. They are important in biology as a source of energy and as structural components in plants.

Source Image: databasefootball.com
Download Image
What are the products of glycolysis? – Quora Jul 31, 2022Molecular Structures. Carbohydrates can be represented by the formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule.In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate“: the components are carbon (“carbo”) and the components of water (hence, “hydrate”).
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
SOLUTION: Macromolecules google docs – Studypool Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH 2 O) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate“: the components are carbon (“carbo”) and the

Source Image: studypool.com
Download Image
4+ Thousand Carbohydrate Structure Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock Polysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. A polysaccharide may contain anywhere from a few monosaccharides to several thousand monosaccharides. Polysaccharides are also called complex carbohydrates. Polysaccharides have a general formula of \(\ceC_x(H_2O)_y\), where \(x\) is

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Biological Molecules Year 12 A-level Carbohydrates, monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides | Teaching Resources Jan 2, 2024Carbohydrate | Definition, Classification, & Examples | Britannica Home Health & Medicine Anatomy & Physiology Science & Tech carbohydrate biochemistry Cite External Websites Written by Eugene A. Davidson

Source Image: tes.com
Download Image
Biomolecules (Older Video 2016) – YouTube Home Bookshelves General Chemistry Structure & Reactivity in Organic, Biological and Inorganic Chemistry (Schaller) Structure & Reactivity in Organic, Biological and Inorganic Chemistry I: Chemical Structure and Properties
Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
What Are Monomers Of Carbohydrates? – Database Football
Biomolecules (Older Video 2016) – YouTube A monosaccharide, the monomer of carbohydrates, is a simple sugar such as fructose or glucose. Fructose is mostly found in fruits, whereas glucose generally results from the digestion of other carbohydrates. Glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6) is used for energy by the cells of most organisms and is a product of photosynthesis. Discuss further with Flexi
SOLUTION: Macromolecules google docs – Studypool Biological Molecules Year 12 A-level Carbohydrates, monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides | Teaching Resources Polysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. A polysaccharide may contain anywhere from a few monosaccharides to several thousand monosaccharides. Polysaccharides are also called complex carbohydrates. Polysaccharides have a general formula of \(\ceC_x(H_2O)_y\), where \(x\) is